High-quality genome of allotetraploid Avena barbata provides insights into the origin and evolution of B subgenome in Avena
- 1. College of Life Sciences, Institute of Life Science and Green Development, Hebei University, Baoding 071000, China
2. Hebei Basic Science Center for Biotic Interaction, Hebei University, Baoding 071000, China
3. State Key Laboratory of Plant Environmental Resilience, College of Biological Sciences, China Agricultural University, Beijing 100094, China
†These authors contributed equally to this work.
*Correspondence: Huilong Du (huilongdu@hbu.edu.cn)
Received date: 2024-07-01
Accepted date: 2025-02-24
Online published: 2025-04-14
Supported by
This work was supported by the Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by CAST Grant No. YESS20210080, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.32100500), the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (Grant Nos: C2021201048 and C2023201074) and the Interdisciplinary Research Program of Natural Science of Hebei University (Grant No: 513201422004). The Excellent Youth Research Innovation Team of Hebei University (Grant No. QNTD202401). Funded by the Science and Technology Project of the Hebei Education Department (Grant No. QN2024271).
Abstract
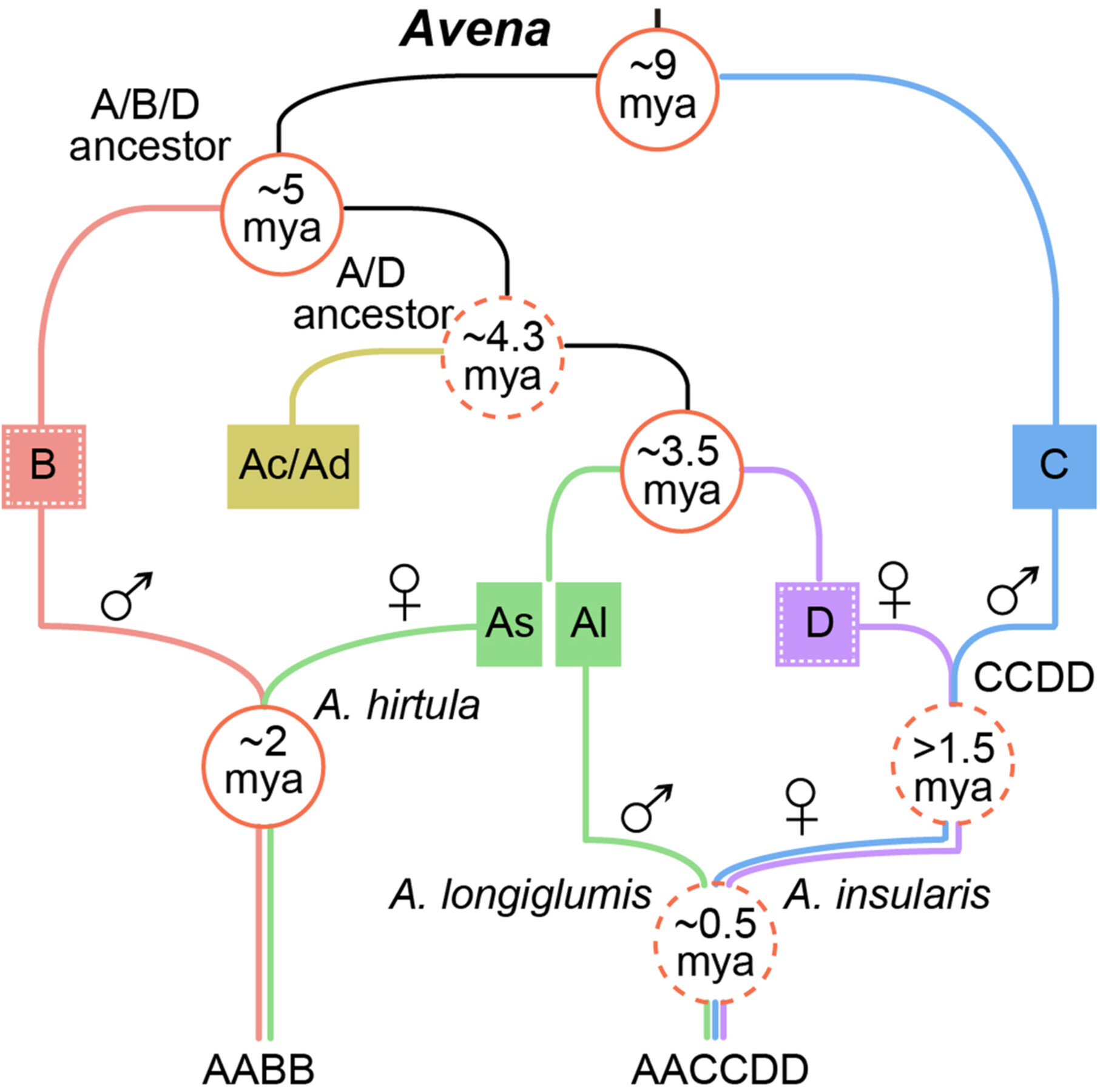
Cite this article
Qiang He, Yao Xiao, Tao Li, Yaru Wang, Yitao Wang, Yu Wang, Wei Li, Ningkun Liu, Zhizhong Gong, Huilong Du . High-quality genome of allotetraploid Avena barbata provides insights into the origin and evolution of B subgenome in Avena[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 0 : 1 . DOI: 10.1111/jipb.13902