

|
||
|
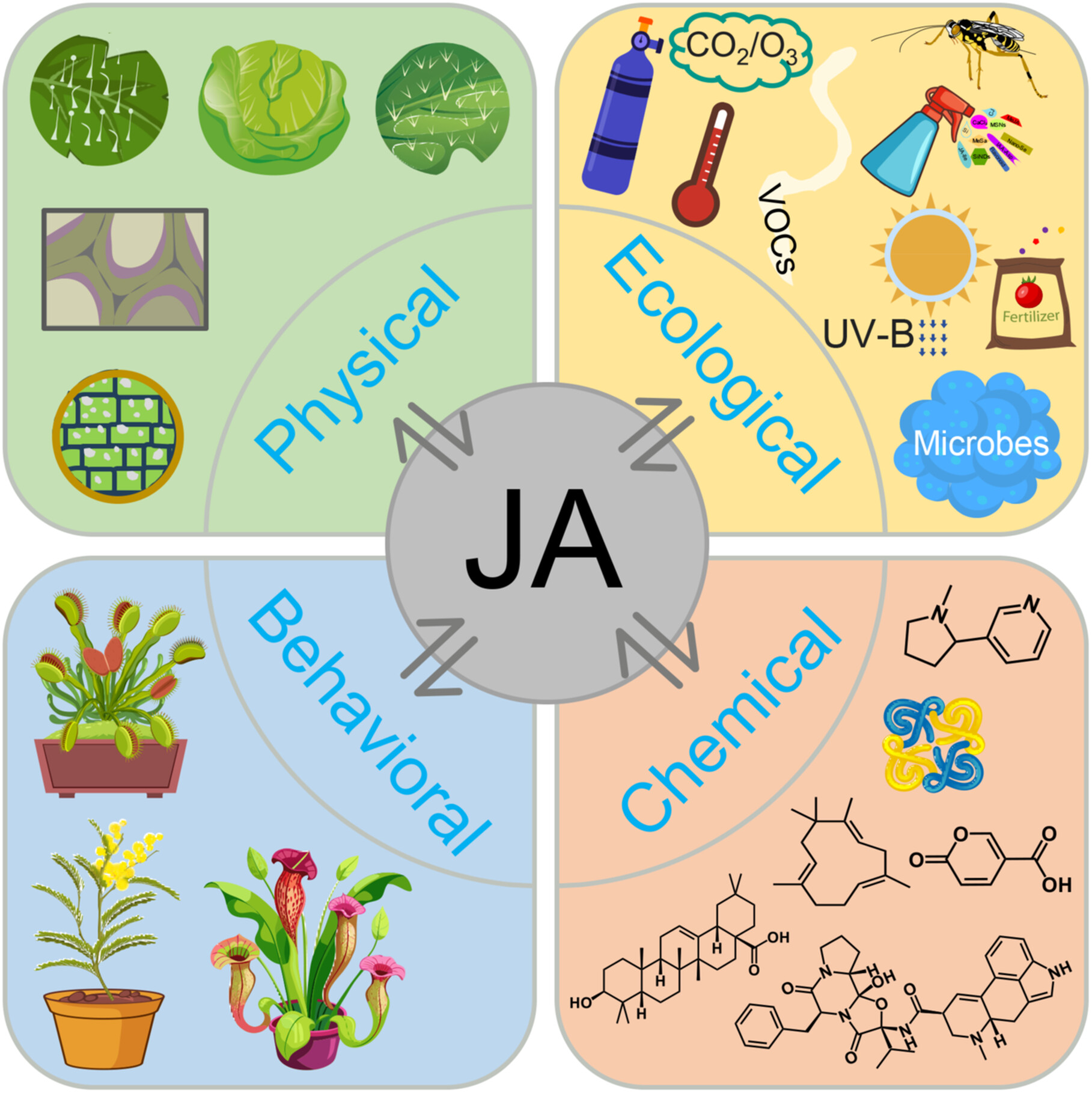
Plant growth and productivity are strongly constrained by herbivorous insects, which reduce both yield and quality. Over the past two centuries, extensive efforts have been devoted to identifying natural insect-resistant. . . | |
|
||
|
||
|
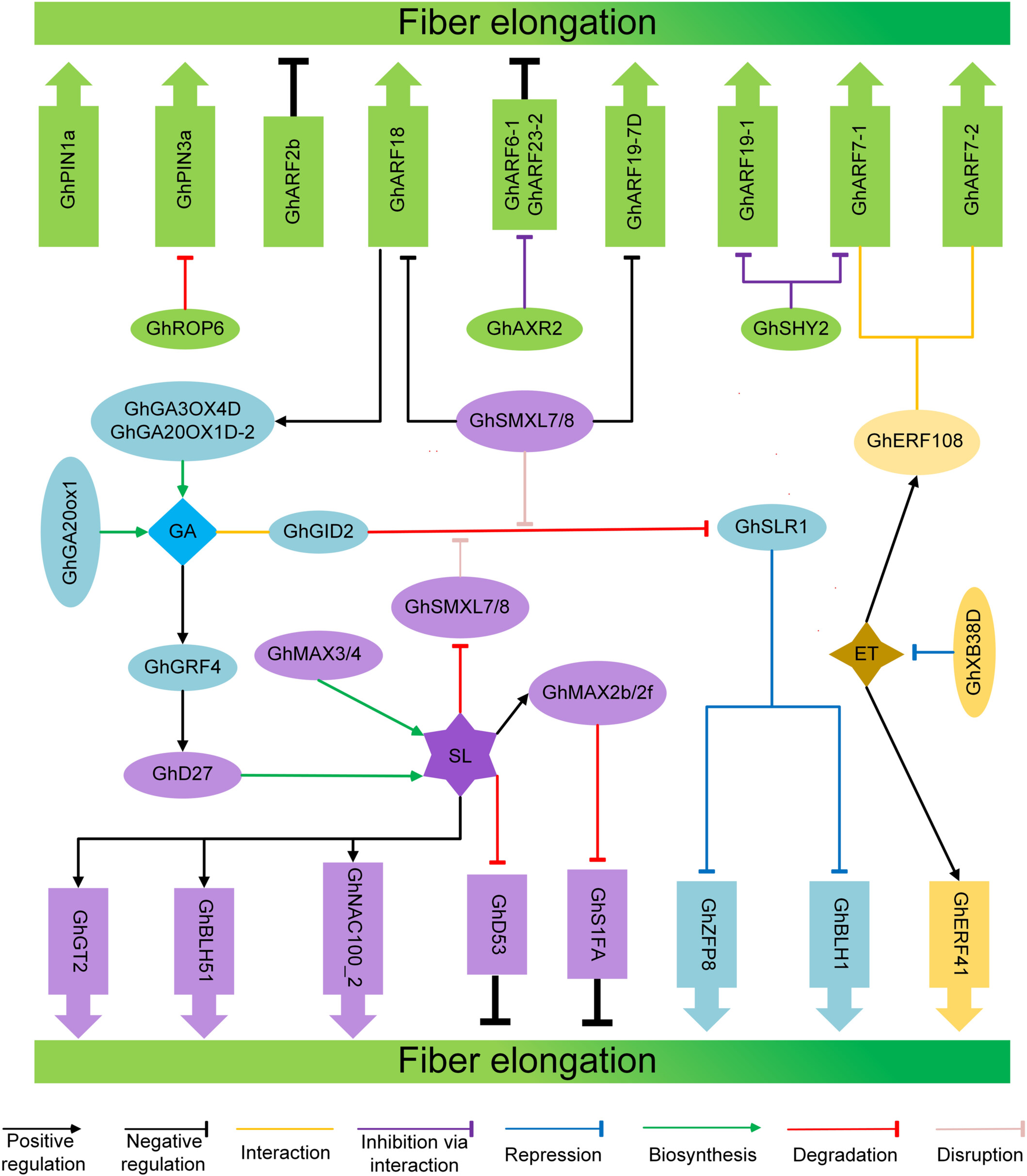
Cotton fiber quality—defined by length, strength, and fineness—directly influences the commercial value of textile products, with fiber length being one of the most critical parameters in industrial procurement. In uplan. . . | |
|
||
| 2026, Vol. 68 | No. 2 | No. 1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2025, Vol. 67 | No.12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 2024, Vol. 66 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 2023, Vol. 65 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 2022, Vol. 64 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 2021, Vol. 63 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 2020, Vol. 62 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 2019, Vol. 61 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 2018, Vol. 60 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 2017, Vol. 59 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 2016, Vol. 58 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 2015, Vol. 57 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 2014, Vol. 56 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 2013, Vol. 55 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 2012, Vol. 54 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 2011, Vol. 53 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 2010, Vol. 52 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 4 | No. 5 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 2009, Vol. 51 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 2008, Vol. 50 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 2007, Vol. 49 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 2006, Vol. 48 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 2005, Vol. 47 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 2004, Vol. 46 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 2003, Vol. 45 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. Suppl. | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 |
| No. 7 | No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | |
| No. 1 | ||||||
| 2002, Vol. 44 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 2001, Vol. 43 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 2000, Vol. 42 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 1999, Vol. 41 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 1998, Vol. 40 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 1997, Vol. 39 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 1996, Vol. 38 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 1995, Vol. 37 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 1994, Vol. 36 | No. Suppl. | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 |
| No. 7 | No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | |
| No. 1 | ||||||
| 1993, Vol. 35 | No. Suppl. | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 |
| No. 7 | No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | |
| No. 1 | ||||||
| 1992, Vol. 34 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 1991, Vol. 33 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 1990, Vol. 32 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 1989, Vol. 31 | No. 12 | No. 11 | No. 10 | No. 9 | No. 8 | No. 7 |
| No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | |
| 1988, Vol. 30 | No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 |
| 1987, Vol. 29 | No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 |
| 1986, Vol. 28 | No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 |
| 1985, Vol. 27 | No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 |
| 1984, Vol. 26 | No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 |
| 1983, Vol. 25 | No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 |
| 1982, Vol. 24 | No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 |
| 1981, Vol. 23 | No. 6 | No. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 |
| 1980, Vol. 22 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | ||
| 1979, Vol. 21 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | ||
| 1978, Vol. 20 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | ||
| 1977, Vol. 19 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | ||
| 1976, Vol. 18 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | ||
| 1975, Vol. 17 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | ||
| 1974, Vol. 16 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | ||
| 1973, Vol. 15 | No. 2 | No. 1 | ||||
| 1966, Vol. 14 | No. 2 | No. 1 | ||||
| 1965, Vol. 13 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | ||
| 1964, Vol. 12 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | ||
| 1963, Vol. 11 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | ||
| 1962, Vol. 10 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | ||
| 1961, Vol. 9 | No. 3 | |||||
| 1960, Vol. 9 | No. 2 | No. 1 | ||||
| 1959, Vol. 8 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | ||
| 1958, Vol. 7 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | ||
| 1957, Vol. 6 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | ||
| 1956, Vol. 5 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | ||
| 1955, Vol. 4 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | ||
| 1954, Vol. 3 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | ||
| 1953, Vol. 2 | No. 4 | No. 3 | No. 2 | No. 1 | ||
| 1952, Vol. 1 | No. 2 | No. 1 |
| J Integr Plant Biol. 2020 Vol. 62 (8): 1132-1158 doi: 10.1111/jipb.12894 |
|
|
| 相关文章 | 多维度评价 |
| J Integr Plant Biol. 2020 Vol. 62 (1): 25-54 doi: 10.1111/jipb.12899 |
|
|
| 相关文章 | 多维度评价 |
| J Integr Plant Biol. 2020 Vol. 62 (8): 1159-1175 doi: 10.1111/jipb.12902 |
|
|
| 相关文章 | 多维度评价 |
| A Cytological Study of Plastid Inheritance in Angiosperms |
| Hu Shi-yi |
| J Integr Plant Biol. 1997 Vol. 39 (4): 363-371 |
|
|
| 相关文章 | 多维度评价 |
| J Integr Plant Biol. 2020 Vol. 62 (8): 1065-1079 doi: 10.1111/jipb.12891 |
|
|
| 相关文章 | 多维度评价 |
| Infrageneric and Sectional Relationships in the Genus Rhododendron(Ericaceae) Inferred from ITS Sequence Data |
| GAO Lian Ming, LI De Zhu, ZHANG Chang Qin, YANG Jun Bo |
| J Integr Plant Biol. 2002 Vol. 44 (11): 1351-1356 |
|
|
| 相关文章 | 多维度评价 |
| J Integr Plant Biol. 2020 Vol. 62 (1): 148-159 doi: 10.1111/jipb.12879 |
|
|
| 相关文章 | 多维度评价 |
| Growth and Morphological Structure of Trapa acornis Seedlings |
| Yan Su-zhen, Xu Xiang-sheng, Chang Fu-chen and Du Kai-he |
| J Integr Plant Biol. 1994 Vol. 36 (Suppl.): null-null |
|
|
| 相关文章 | 多维度评价 |
| J Integr Plant Biol. 2019 Vol. 61 (12): 1201-1205 doi: 10.1111/jipb.12774 |
|
|
| 相关文章 | 多维度评价 |
| J Integr Plant Biol. 2020 Vol. 62 (4): 433-455 doi: 10.1111/jipb.12877 |
|
|
| 相关文章 | 多维度评价 |
| Developmental Mechanism and Distribution Pattern of Stomatal Clusters in Begonia peltatifolia |
| TANG Min, HU Yu Xi, LIN Jin Xing, JIN Xiao Bai |
| J Integr Plant Biol. 2002 Vol. 44 (4): 384-390 |
|
|
| 相关文章 | 多维度评价 |
| Contributions of Chinese Botanists to Plant Tissue Culture in the 20th Century |
| CHU Chih-Ching |
| J Integr Plant Biol. 2002 Vol. 44 (9): 1075-1084 |
|
|
| 相关文章 | 多维度评价 |
| The Distribution of Stomata and Photosynthetic Pathway in Leaves |
| Lin Zhi-fang, Li Shuang-shun and Lin Gui-zhu |
| J Integr Plant Biol. 1986 Vol. 28 (4): null-null |
|
|
| 相关文章 | 多维度评价 |
| Plant terpenoids: Biosynthesis and ecological functions |
| Ai-Xia Cheng, Yong-Gen Lou, Ying-Bo Mao, Shan Lu, Ling-Jian Wang and Xiao-Ya Chen |
| J Integr Plant Biol. 2007 Vol. 49 (2): 179-186 doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2007.00395.x |
|
|
| 相关文章 | 多维度评价 |
| The plant vascular system: Evolution, development and functions |
| William J. Lucas, Andrew Groover, Raffael Lichtenberger, Kaori Furuta, Shri-Ram Yadav, Ykä Helariutta, Xin-Qiang He, Hiroo Fukuda, Julie Kang, Siobhan M. Brady, John W. Patrick, John Sperry, Akiko Yoshida, Ana-Flor López-Millón, Michael A. Grusak, and Pradeep Kachroo |
| J Integr Plant Biol. 2013 Vol. 55 (4): 294-388 doi: 10.1111/jipb.12041 |
|
|
| 相关文章 | 多维度评价 |
| Rice Research: Past, Present and Future |
| Hong Ma, Kang Chong and Xing-Wang Deng |
| J Integr Plant Biol. 2007 Vol. 49 (6): 729-730 doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2007.00515.x |
|
|
| 相关文章 | 多维度评价 |
| Анатомическое исследование природного древесного угля ,полученного врайоне Чанбайщана |
| Гу он-гэн |
| J Integr Plant Biol. 1957 Vol. 6 (2): null-null |
|
|
| 相关文章 | 多维度评价 |
| The Structure Anomalous Secondary Growth of Stem in Gnetum montanum |
| Gao Xin-zeng, Chen Yao-tang, Deng Yue-fen and Li Rong-ao |
| J Integr Plant Biol. 1984 Vol. 26 (6): null-null |
|
|
| 相关文章 | 多维度评价 |
| Advances in the Studies on Water Uptake by Plant Roots |
| ZHAO Chang-Xing, DENG Xi-Ping, ZHANG Sui-Qi, YE Qing, Ernst STEUDLE, SHAN Lun |
| J Integr Plant Biol. 2004 Vol. 46 (5): 505-514 |
|
|
| 相关文章 | 多维度评价 |
| Isolation of Rice EPSP Synthase cDNA and Its Sequence Analysis and Copy Number Determination |
| XU Jun-Wang, WEI Xiao-Li, LI Xu-Gang, CHEN Lei, FENG De-Jiang and ZHU Zhen |
| J Integr Plant Biol. 2002 Vol. 44 (2): 188-192 |
|
|
| 相关文章 | 多维度评价 |
| Phototropins and Their LOV Domains: Versatile Plant Blue-Light Receptors |
| Winslow R. Briggs, Tong-Seung Tseng, Hae-Young Cho, Trevor E. Swartz, Stuart Sullivan, Roberto A. Bogomolni, Eirini Kaiserli and John M. Christie |
| J Integr Plant Biol. 2007 Vol. 49 (1): 4 -10 doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2006.00406.x |
|
|
| 相关文章 | 多维度评价 |
| 被引次数: Baidu(793) |
| Functions and Application of the AP2/ERF Transcription Factor Family in Crop Improvement |
| Zhao-Shi Xu, Ming Chen, Lian-Cheng Li and You-Zhi Ma |
| J Integr Plant Biol. 2011 Vol. 53 (7): 570 -585 doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2011.01062.x |
|
|
| 相关文章 | 多维度评价 |
| 被引次数: Baidu(403) |
| Global Change Effects on Plant Chemical Defenses against Insect Herbivores |
| M. Gabriela Bidart-Bouzat and Adebobola Imeh-Nathaniel |
| J Integr Plant Biol. 2008 Vol. 50 (11): 1339 -1354 doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2008.00751.x |
|
|
| 相关文章 | 多维度评价 |
| 被引次数: Baidu(374) |
| Molecular analysis of legume nodule development and autoregulation |
| Brett J. Ferguson, Arief Indrasumunar, Satomi Hayashi, Meng-Han Lin, Yu-Hsiang Lin, Dugald E. Reid and Peter M. Gresshoff |
| J Integr Plant Biol. 2010 Vol. 52 (1): 61 -76 doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2010.00899.x |
|
|
| 相关文章 | 多维度评价 |
| 被引次数: Baidu(364) |
| Reactive Oxygen Species during Plant-microorganism Early Interactions |
| Amrit K Nanda, Emilie Andrio, Daniel Marino, Nicolas Pauly, and Christophe Dunand |
| J Integr Plant Biol. 2010 Vol. 52 (2): 195 -204 doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2010.00933.x |
|
|
| 相关文章 | 多维度评价 |
| 被引次数: Baidu(354) |
| Thermal Hardening: A New Seed Vigor Enhancement Tool in Rice |
| Muhammad FAROOQ, S. M. A. BASRA, Nazir AHMAD and K. HAFEEZ |
| J Integr Plant Biol. 2005 Vol. 47 (2): 187 -193 doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2005.00031.x |
|
|
| 相关文章 | 多维度评价 |
| 被引次数: Baidu(343) |
| How plants cope with cadmium: Staking all on metabolism and gene expression |
| Giovanni DalCorso, Silvia Farinati, Silvia Maistri and Antonella Furini |
| J Integr Plant Biol. 2008 Vol. 50 (10): 1268 -1280 doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2008.00737.x |
|
|
| 相关文章 | 多维度评价 |
| 被引次数: Baidu(342) |
| The WRKY Gene Family in Rice (Oryza sativa) |
| Christian A. Ross, Yue Liu and Qingxi J. Shen |
| J Integr Plant Biol. 2007 Vol. 49 (6): 827 -842 doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2007.00504.x |
|
|
| 相关文章 | 多维度评价 |
| 被引次数: Baidu(339) |
| Abscisic Acid-mediated Epigenetic Processes in Plant Development and Stress Responses |
| Viswanathan Chinnusamy, Zhizhong Gong and Jian-Kang Zhu |
| J Integr Plant Biol. 2008 Vol. 50 (10): 1187 -1195 doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2008.00727.x |
|
|
| 相关文章 | 多维度评价 |
| 被引次数: Baidu(336) |
| Metabolism and Long-distance Translocation of Cytokinins |
| Toru Kudo, Takatoshi Kiba and Hitoshi Sakakibara |
| J Integr Plant Biol. 2010 Vol. 52 (1): 53 -60 doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2010.00898.x |
|
|
| 相关文章 | 多维度评价 |
| 被引次数: Baidu(335) |
